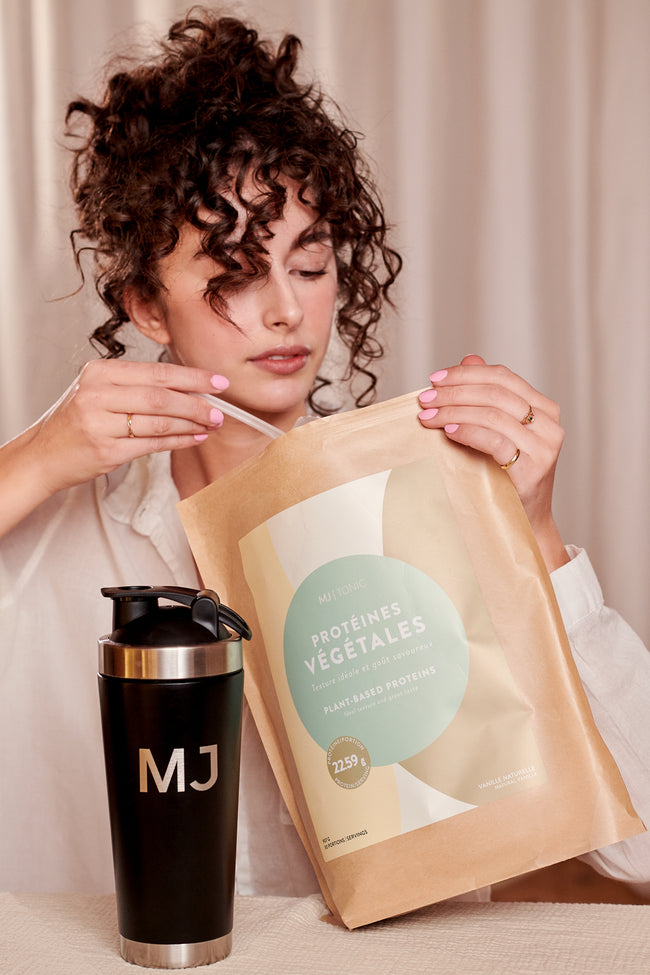
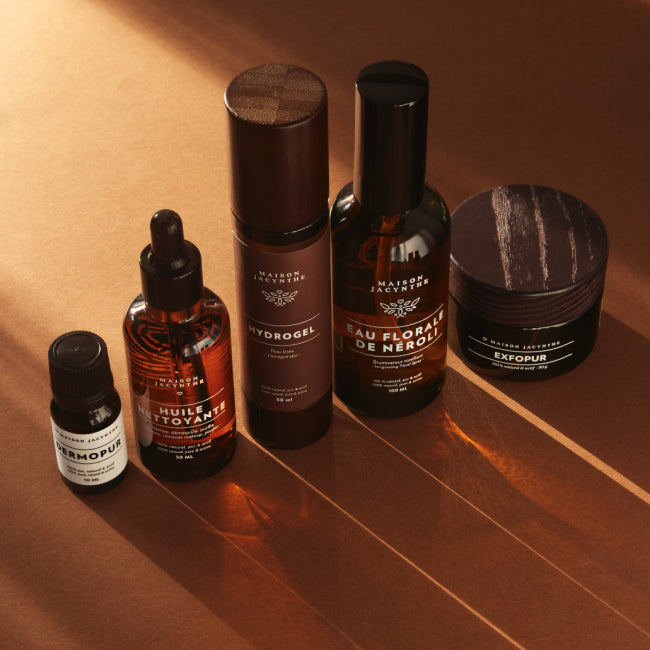
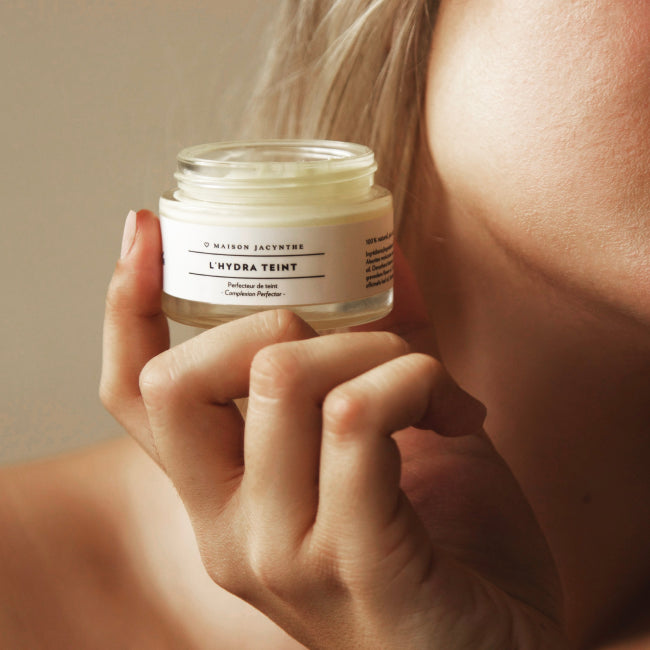
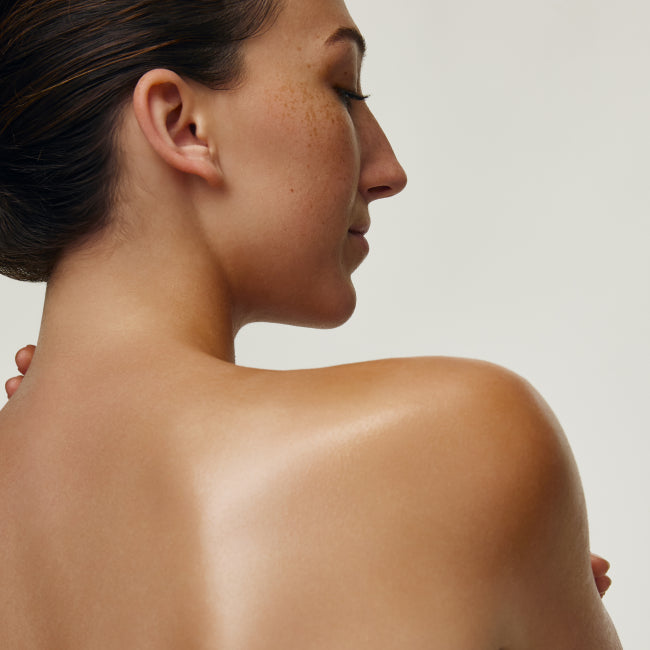
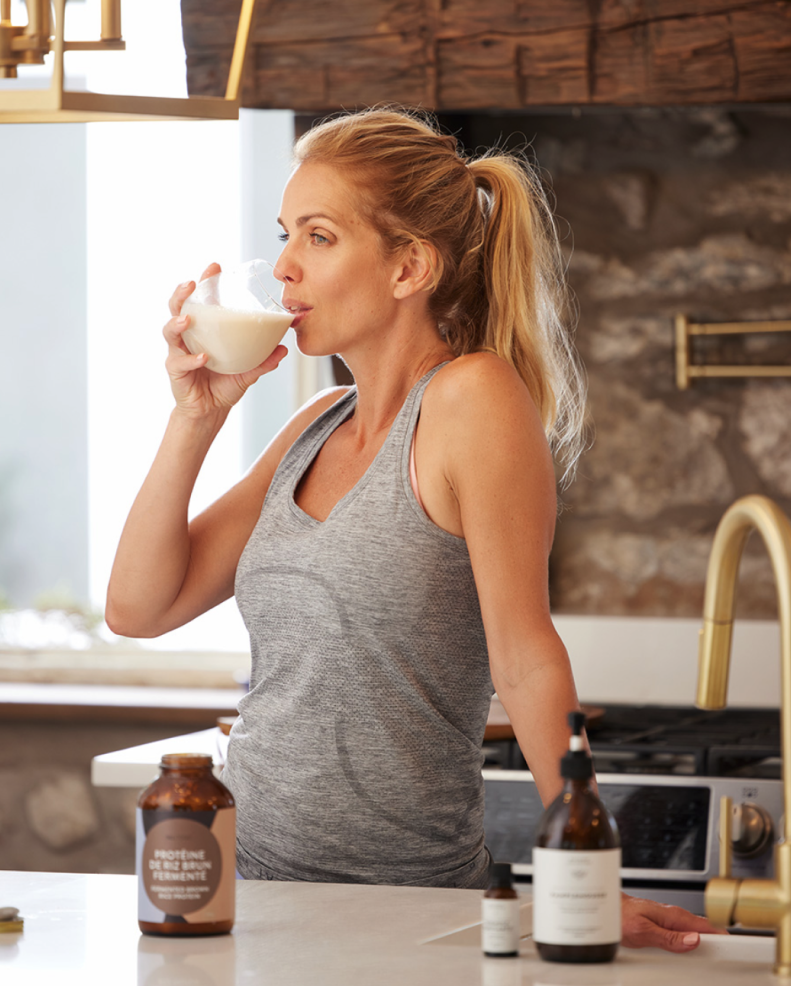
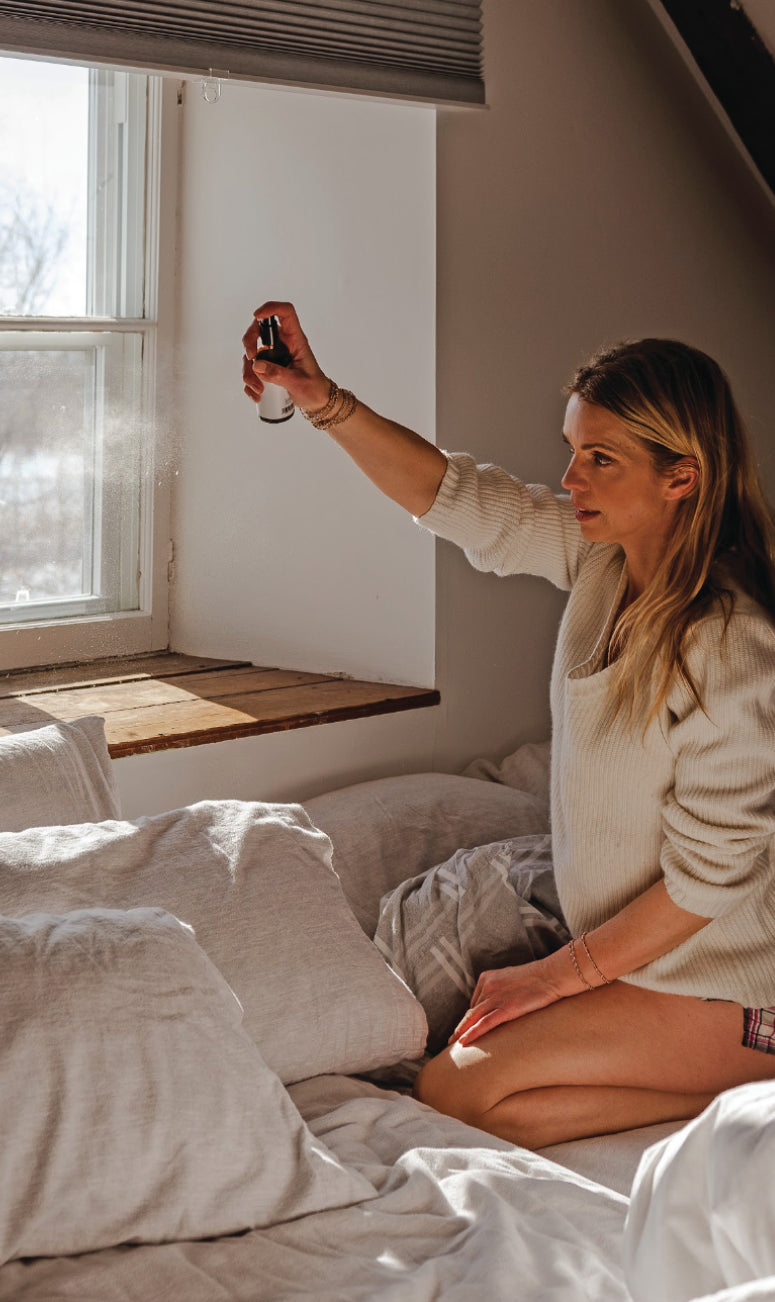
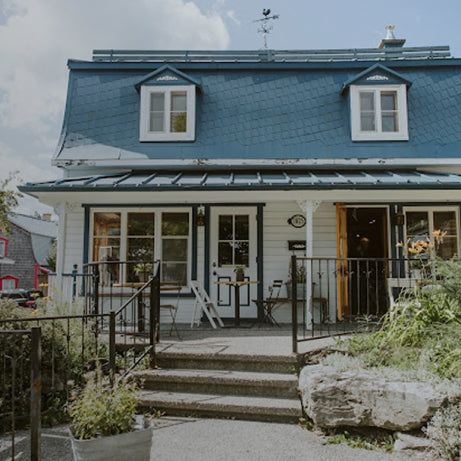
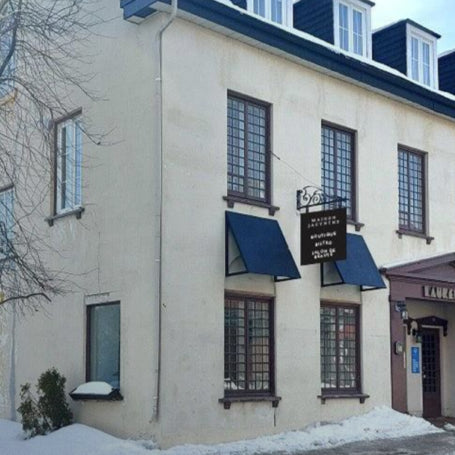
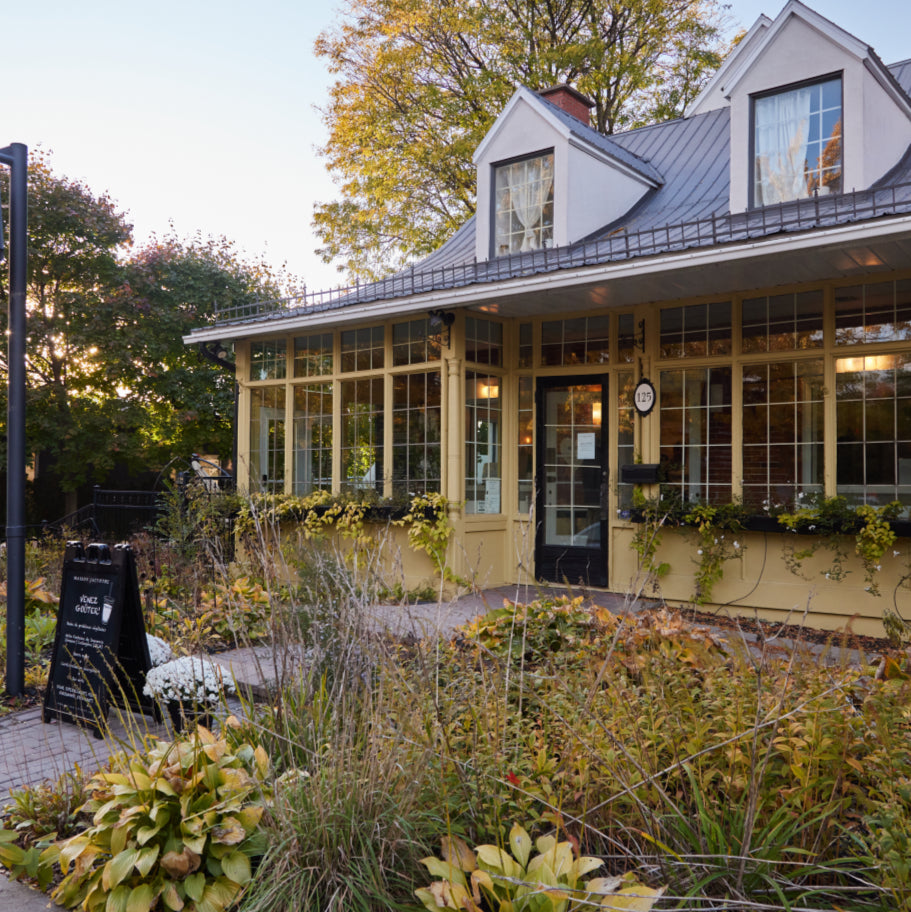
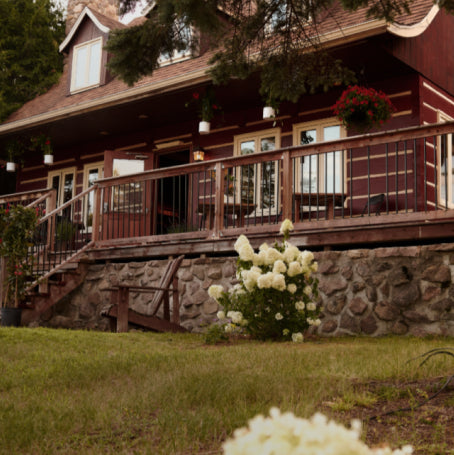
« Maison Jacynthe utilise les ingrédients les plus purs, issus des meilleurs distillateurs du monde avec les meilleures pratiques qui existent »

Selection of essentials
Exclusive
Our services
Each service has been carefully selected by Jacynthe to meet your needs and ensure your well-being.
Shortcuts to your searches
Blog
Read & view by category
Jacynthe gives you her best advice on beauty, nutrition and well-being to help you beautify your daily life.